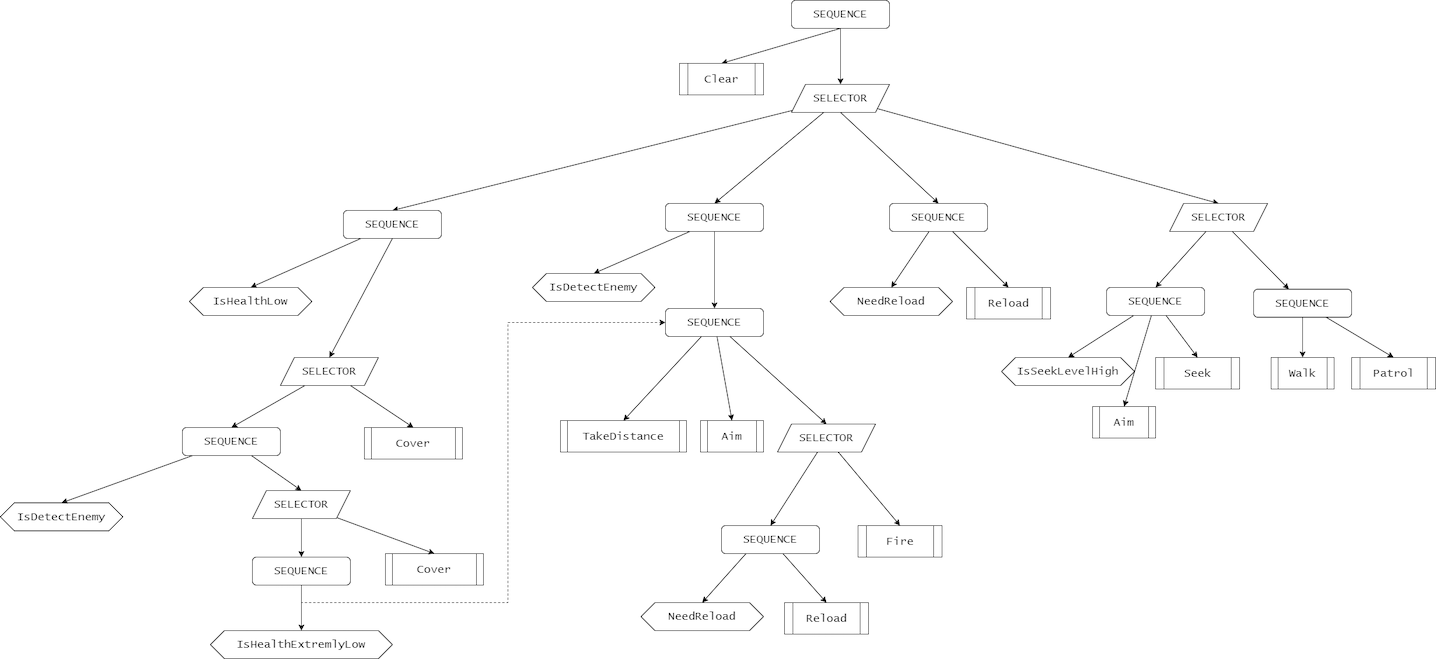
AI Behavior Tree (1)
AI 프로그래밍은 Behavior Tree 를 사용할 것이다.
원래 FSM 으로도 구현했으나, 점점 스파게티 코드가 되어가는 것을 보고...
Behavior Tree 로 갈아타기로 했다.
앞으로 더 추가될 예정이지만 일단 간단하게 FlowChart 를 그려 보았다.
Base 구현
Node
namespace BT
{
public enum NodeState
{
RUNNING,
SUCCESS,
FAILURE
}
public class Node
{
public NodeState state;
protected BehaviorTree bt;
protected List<Node> children;
public Node()
{
this.bt = null;
this.children = new List<Node>();
}
public Node(BehaviorTree bt)
{
this.bt = bt;
this.children = new List<Node>();
}
public Node(List<Node> children)
{
this.bt = null;
this.children = children;
}
public virtual NodeState Evaluate() => NodeState.FAILURE;
}
}
BehaviorTree 레퍼런스를 가지고 있는 이유는 Node 간 공유하는 변수에 접근하기 위해서이다.
Selector
namespace BT
{
public class Selector : Node
{
public Selector() : base() {}
public Selector(List<Node> children) : base(children) {}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
foreach (Node child in children)
{
switch (child.Evaluate())
{
case NodeState.RUNNING:
state = NodeState.RUNNING;
return state;
case NodeState.SUCCESS:
state = NodeState.SUCCESS;
return state;
case NodeState.FAILURE:
continue;
}
}
state = NodeState.FAILURE;
return state;
}
}
}
Sequence
namespace BT
{
public class Sequence : Node
{
public Sequence() : base() {}
public Sequence(List<Node> children) : base(children) {}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
bool anyRunning = false;
foreach (Node child in children)
{
switch (child.Evaluate())
{
case NodeState.RUNNING:
anyRunning = true;
continue;
case NodeState.SUCCESS:
continue;
case NodeState.FAILURE:
state = NodeState.FAILURE;
return state;
}
}
state = anyRunning ? NodeState.RUNNING : NodeState.SUCCESS;
return state;
}
}
}
EnemyRobotBT
위에서 정의한 BehaviorTree 클래스를 상속받아 사용한다.
public class EnemyRobotBT : BehaviorTree
{
[NonSerialized]
public EnemyRobotAI ai;
private void Awake()
{
ai = GetComponent<EnemyRobotAI>();
}
protected override Node CreateTree()
{
Node root = new Sequence();
return root;
}
public void OnDeath()
{
active = false;
}
}
앞으로 만들 Task 와 Check 노드들이 전부 root 노드에 Child 로 들어가면 된다.